Quick Summary
What began as a grocery store experiment in the 1940s is now the backbone of global supply chain visibility. Barcodes have evolved from simple lines to data-rich 2D/3D codes, driving unprecedented accuracy and real-time tracking. With innovations like AR-guided warehouses and RFID hybrids, they’re proving even the smallest label can pack a billion-dollar punch.
Introduction: The Silent Workhorse of Modern Logistics
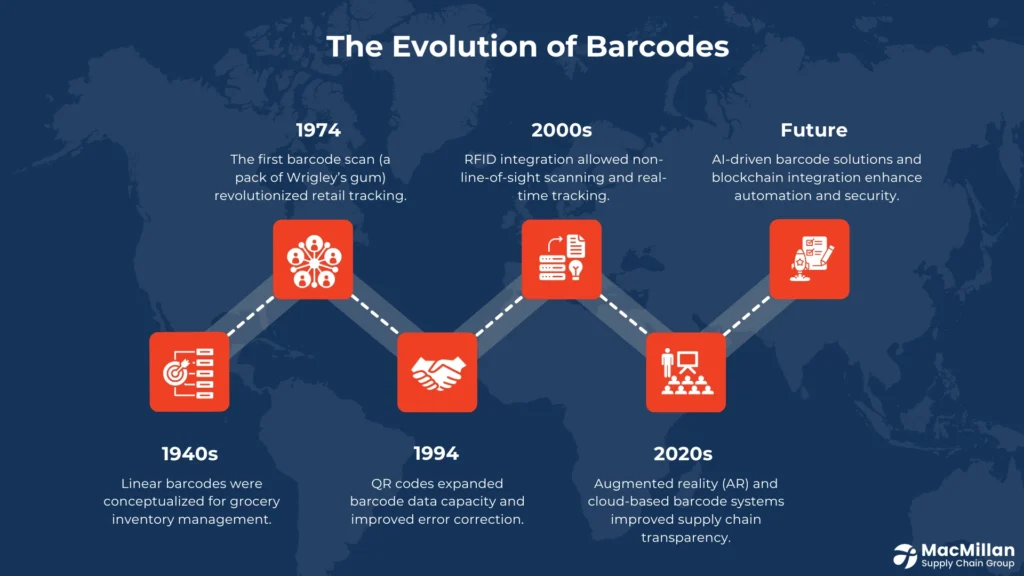
Picture a world without barcodes: checkout lines snaking through stores, shipments lost in transit chaos, and inventory counts buried in guesswork. Thankfully, we don’t live there. Since that first beep scanning a pack of Wrigley’s gum in 1974, barcodes have quietly transformed supply chain visibility into precision engines. Today, they’re not just identifiers they’re data powerhouses, merging with AI and IoT to turn logistics into a science.
The Evolution of Barcodes
The journey of barcodes began with humble linear codes in the 1940s, initially designed for inventory management in grocery stores. These rudimentary designs, consisting of parallel lines, paved the way for the Universal Product Code (UPC) system, which revolutionized retail operations when the first item was scanned in 1974. This pivotal moment marked the widespread adoption of barcodes, simplifying product tracking and inventory management across various sectors.
Two-dimensional (2D) barcodes were created as a result of the limits of linear codes becoming evident as technology developed. With the addition of strong errors correcting mechanisms, these cutting-edge designs such as QR codes and Data Matrix codes significantly expanded data storage capacities and ensured dependable reading even on damaged or obscured codes.
Modern Trends in Barcode Technology
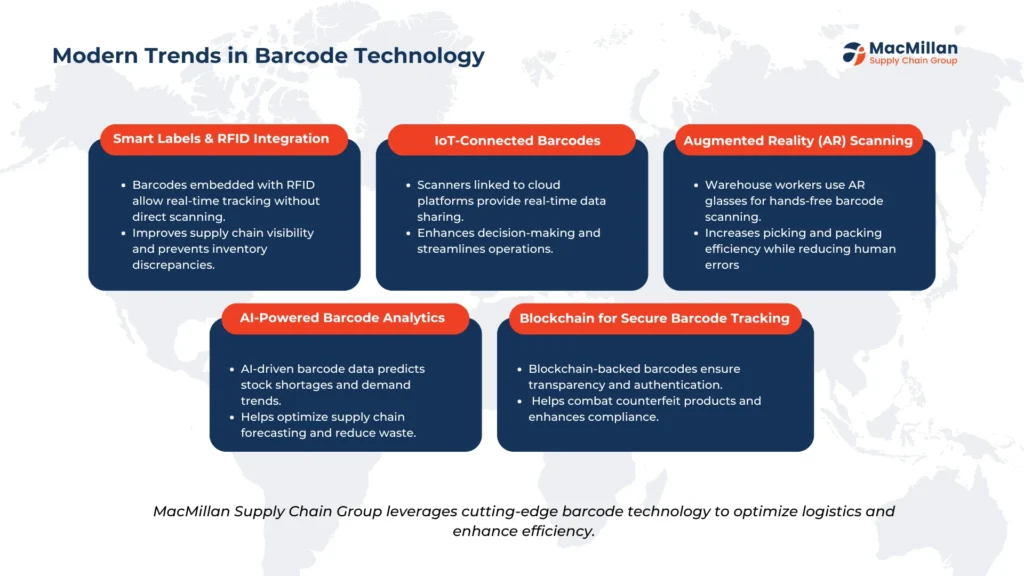
Contemporary barcode technology goes far beyond simple item identification. Advanced systems now integrate sensors, artificial intelligence (AI), and augmented reality (AR) to automate scanning processes and improve accuracy dramatically. AR applications, for instance, enable seamless inventory management by displaying digital information within a worker’s direct line of vision, reducing errors in picking and packing operations.
Additionally, the advent of “smart labels” and Internet of Things (IoT) integration has revolutionized supply chain visibility. These intelligent barcodes, equipped with sensors and wireless connectivity, provide real-time tracking of products throughout the entire logistics journey, from manufacturing to final delivery. This level of transparency aligns with modern trends prioritizing optimization and end-to-end supply chain oversight.
Industry Specific Innovations: Beyond Retail
Different sectors have harnessed barcodes in unique ways, tailoring the technology to their challenges:
Healthcare: Data Matrix codes, with their high reliability, track every pill and medical device. Hospitals use them to prevent counterfeit drugs and ensure compliance with stringent regulations. During the COVID-19 pandemic, these codes were critical in managing vaccine distribution.
Retail: QR codes bridge online and offline experiences. A customer scanning a code on a clothing tag might see a video of the garment’s sustainable production process or access exclusive discounts, fostering brand loyalty.
Manufacturing: Centralized systems sync barcode data across global factories, ensuring components arrive just-in-time. Toyota, for example, slashed production delays by 30% using real time part tracking.
These applications highlight barcodes’ versatility they’re not just tools for logistics but catalysts for innovation.
RFID and Barcode Integration
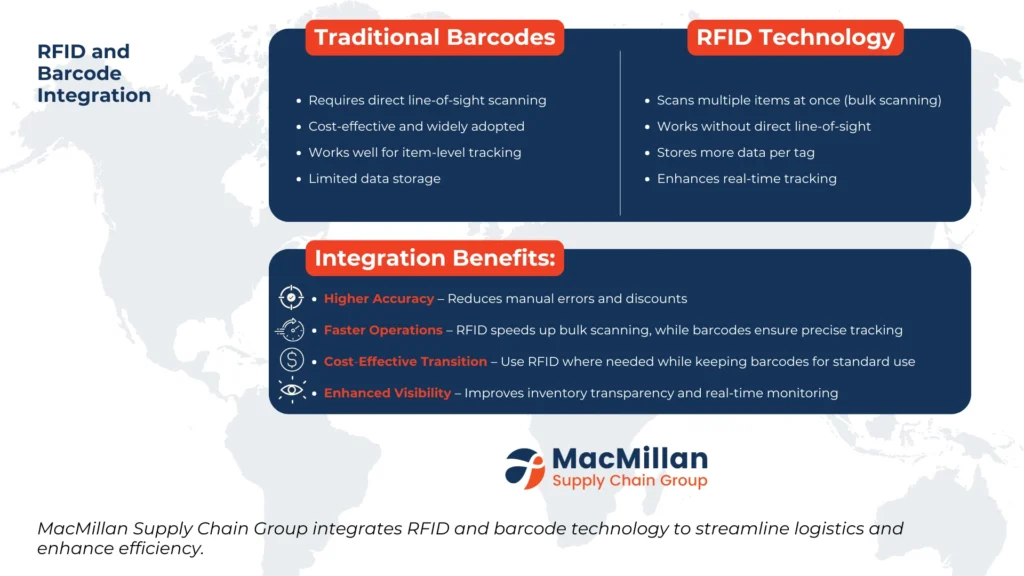
The integration of radio frequency identification (RFID) technology with traditional barcodes represents a significant leap forward in logistics innovation. By combining RFID’s non-line-of-sight capability with the data capacity of barcodes, businesses can implement faster and more efficient scanning solutions. This hybrid approach addresses the logistical challenges of modern supply chain visibility, emphasizing the necessity for continuous innovation in inventory management.
Common Hurdles (and How to Clear Them)
- Legacy Scanner Woes: Older devices can’t read 2D codes? Retrofit with add-on lenses.
- Upgrade Costs: Start with pilot projects—e.g., tag high-value items first.
- Data Silos: Cloud platforms unify scanning data across teams.
MacMillan’s Fix:
- Phased Upgrades: Modernize scanners without breaking budgets.
- Staff Training: Turn skeptics into barcode pros with hands-on workshops.
- Custom Tools: APIs that sync barcode data with your existing ERP..
We also provide comprehensive training and support services to ensure your staff maximizes the efficiency of barcode deployments. Our experts work closely with your team to streamline processes, enhance data management practices, and implement best practices for supply chain visibility and accuracy
Implementing Solutions: Work with MacMillan
To stay ahead in the rapidly evolving landscape of supply chain management, partnering with industry experts is crucial. MacMillan Supply Chain combines deep domain expertise with state-of-the-art technology to deliver optimized logistics solutions tailored to your specific needs.
By leveraging our advanced barcode and RFID integration capabilities, you can future-proof your operations, ensuring a smooth transition to emerging technologies while maximizing the value of your existing investments. Contact us today to explore how we can streamline your supply chain, enhance visibility, and drive operational excellence through the power of innovative barcode solutions.
FAQs
Compared to its linear predecessors, 2D barcodes—such as QR codes and Data Matrix codes offer a number of benefits. These include extra storage space for data, strong error-correction systems, and the ability to record more specific product details like batch numbers and manufacture dates. 2D barcodes are useful for marketing and brand engagement campaigns since they also allow for richer consumer connection through smartphone scanning.
The shift to 2D barcodes is being driven by initiatives like GS1's Sunrise 2027, which aims to enhance supply chain traceability, visibility, and consumer engagement across industries. By adopting 2D barcodes, businesses can leverage their expanded data capabilities to improve inventory accuracy, product authentication, and regulatory compliance, ultimately streamlining logistics operations and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Augmented reality (AR) applications play a significant role in improving warehouse operations and supply chain management. By displaying digital information within a worker's direct line of vision, AR solutions can guide employees through picking, packing, and inventory management tasks, reducing errors and increasing productivity. This hands-free approach to barcode scanning and data visualization represents a significant step forward in logistics efficiency.
RFID technology complements traditional barcode systems by allowing non-line-of-sight and bulk scanning capabilities, significantly increasing the speed and efficiency of inventory tracking in logistics and warehousing operations. By combining RFID's ability to read multiple tags simultaneously with the data capacity of barcodes, businesses can implement robust, real-time inventory management solutions that streamline supply chain processes.
This article serves as a comprehensive guide to understanding how the evolution of barcode technology is driving supply chain efficiency and visibility. By staying at the forefront of these advancements, businesses can optimize their logistics operations, reduce costs, and deliver exceptional customer experiences.
At MacMillan Supply Chain, we are committed to helping our clients harness the power of innovative barcode solutions. Contact us today to explore how our expertise and cutting-edge technologies can transform your supply chain, ensuring you remain competitive in today's dynamic marketplace.




